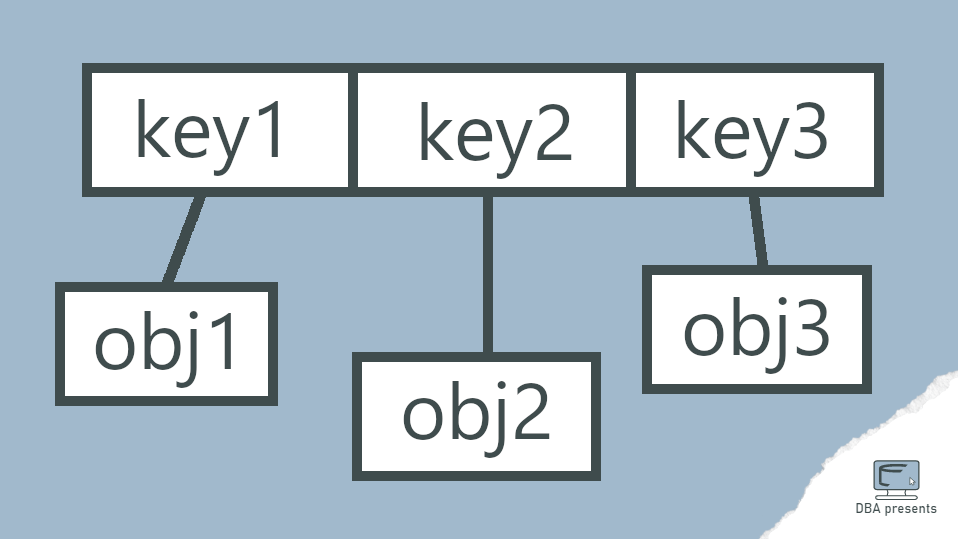
Java Streams are good for manipulating a collection of objects. A classic example of a collection that is often used for streams is a list. Rarely, but still sometimes, we want to transform a list to a map. See how.
Base object
As always, I will demonstrate how to do that in a particular case. A Java Stream must consist of some objects. Why not cities? I define City class.
public class City {
private final Integer id;
private final String name;
public City(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
It contains two fields: id and name.
Now, I am missing a list of cities. I need a few lines more to create a list of cities.
City city1 = new City(1, "Krakow");
City city2 = new City(2, "Gdansk");
List<City> cities = new ArrayList<>();
cities.add(city1);
cities.add(city2);
A list of cities contains two objects. That is enough to say - it is a list.
List to Map using Collectors.toMap
To form a final collection from a stream, we use the collect method. The most commonly built collection from a stream is a list. We do it like that:
cities.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
The above code returns a list of cities. Usually, before forming a list we use filter or map methods to manipulate the stream somehow, but you get the point.
Going further, collecting to map is not much different. Except, it requires defining a key and a value for each element.
Key and value come from object
The simplest case is when the key and value of the final map are already fields on the list of elements. In my case, a key will be a city id and a value will be a city name.
Map<Integer, String> idToName = cities.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(City::getId, City::getName));
I used method references to define the mapping.
Key or value is the original object
Even if the above case was obvious to you, you may wonder how to tell Java that a value (or key) should be the whole original object, not its field. That is nothing difficult; just use a simple lambda.
Map<Integer, City> idToCity = cities.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(City::getId, city -> city));
It creates mapping between a city id and a city object.
Key or value is computed
I am sure, it is not a mystery after the above examples, but to make this text complete. I will also show how to build a map when some computation is required.
Map<String, City> lowerCaseNameToCity = cities.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(city -> city.getName().toLowerCase(), city -> city));
In this case, it builds a map with a lower case city name as a key and a city object as a value.
Any other cases can be done in a very similar way.